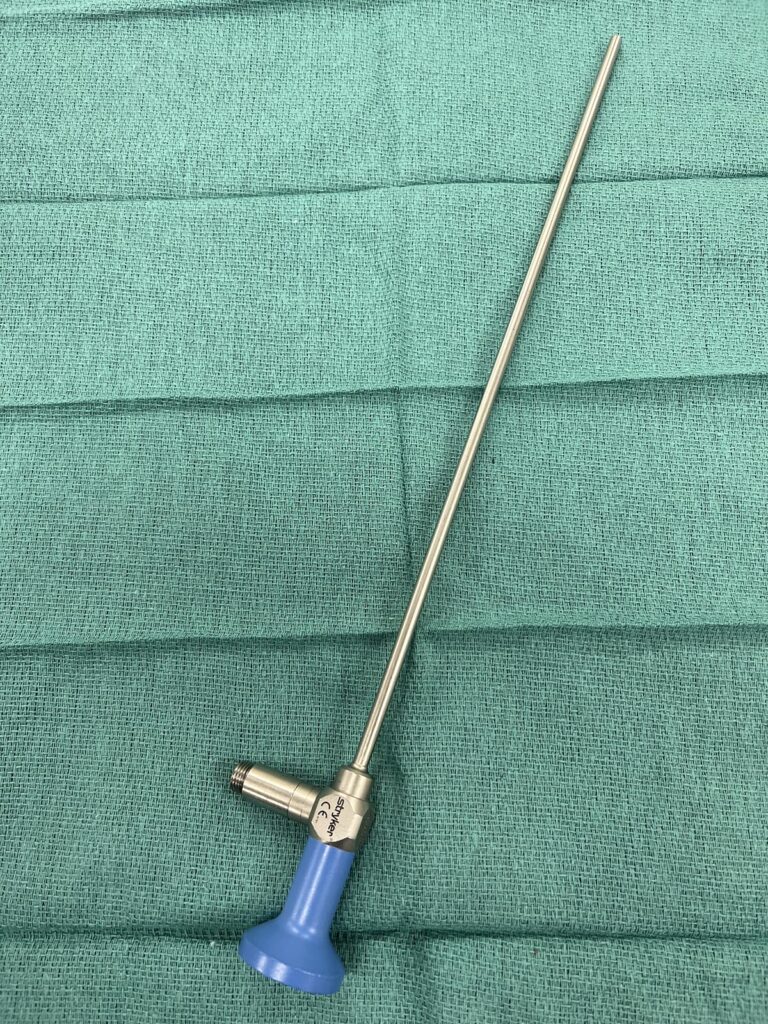
Endoscopes
Endoscopes are the method of visualizing internal organs or structures during MIS procedures. They can be inserted through a natural body orifice (i.e., a colonoscope, cystoscope, ureteroscope, or bronchoscope) or through a small incision (i.e., a laparoscope or arthroscope).
These scopes can be rigid, semi-rigid, or flexible. Some scopes have working channels so that procedures can be performed through them. This includes suction, irrigation, or even the ability to pass instruments through, while others just provide visualization.
Field of View:

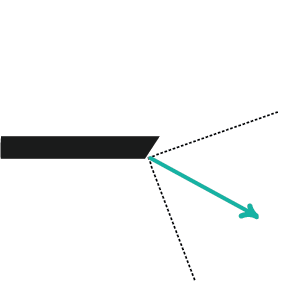
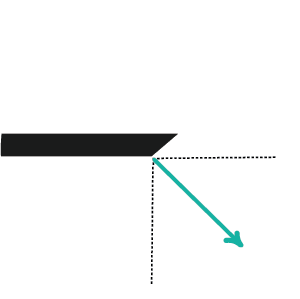
Endoscopes come in varied sizes and diameters, depending on their purpose. Rigid scopes can have the distal lens look straight forward at 0 degrees, or can be angled at 30, 70, or 120 degrees. Because flexible scopes can be angled by the user, they can allow for a panoramic view.
(Ball, 2019)
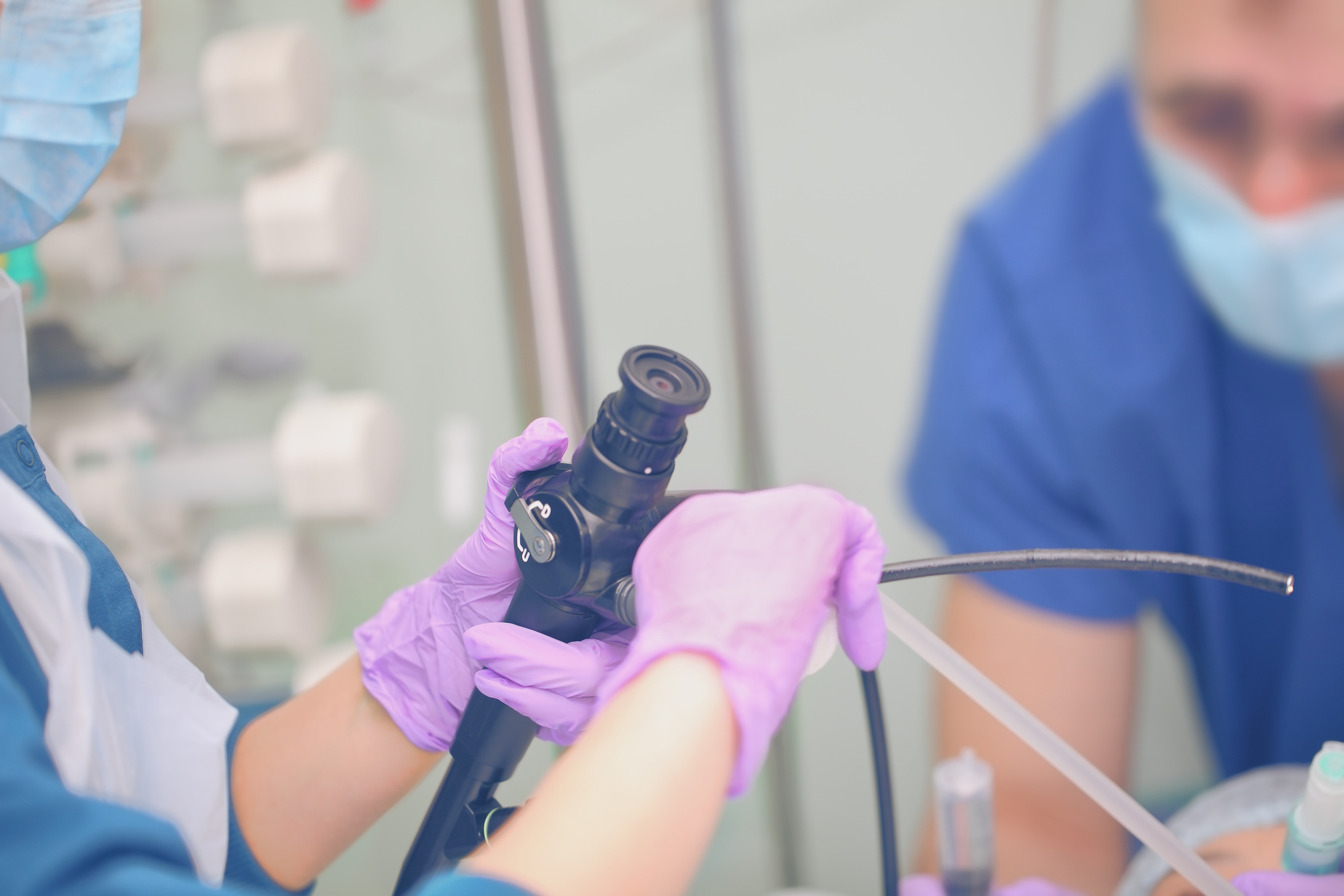
Flexible Endoscopes
Components of a flexible scope:
- Control body: Angulation knobs, air-water channels, biopsy port, eyepiece
- Insertion tube: Flexible tube containing channels for suction, biopsy, irrigation, air and water, image bundles for the fiberscope, and light bundles
- Bending section: Section at the distal tip that has to bend rubber, lenses, air-water nozzle, C-cover, and chip for videoscopes
- Light-guide connector: Suction, air-water channel
Systems within a flexible endoscope:
- Mechanical: Allows ports to introduce accessories to perform treatment and procedures.
- Angulation: Allows the distal tip to move in different directions.
- Illumination: Provides light to view internal structures.
Examples: Angioscopes, Bronchoscopes, Choledochoscopes, Colonoscopes, Cystonephroscopes, Hysteroscopes, and Mediastinoscopes. Ureteroscopes (Ball, 2019)
Rigid Endoscopes
There are four distinct components of a rigid scope:
- Eyepiece: Contains the ocular lens.
- Body: Contains light-guide connector, and valves.
- Shaft: Contains rod lenses and spacers.
- Distal end: Contains objective and negative lenses.
Examples: Cystoscopes, Laparoscopes, Sinuscopes, Arthroscopes, Bronchoscopes, Laryngoscopes, Hysteroscopes
(Ball, 2019)
